TERENO-NE - Northeastern German Lowland Observatory
Contact:
Web:
Infrastructure belongs to:
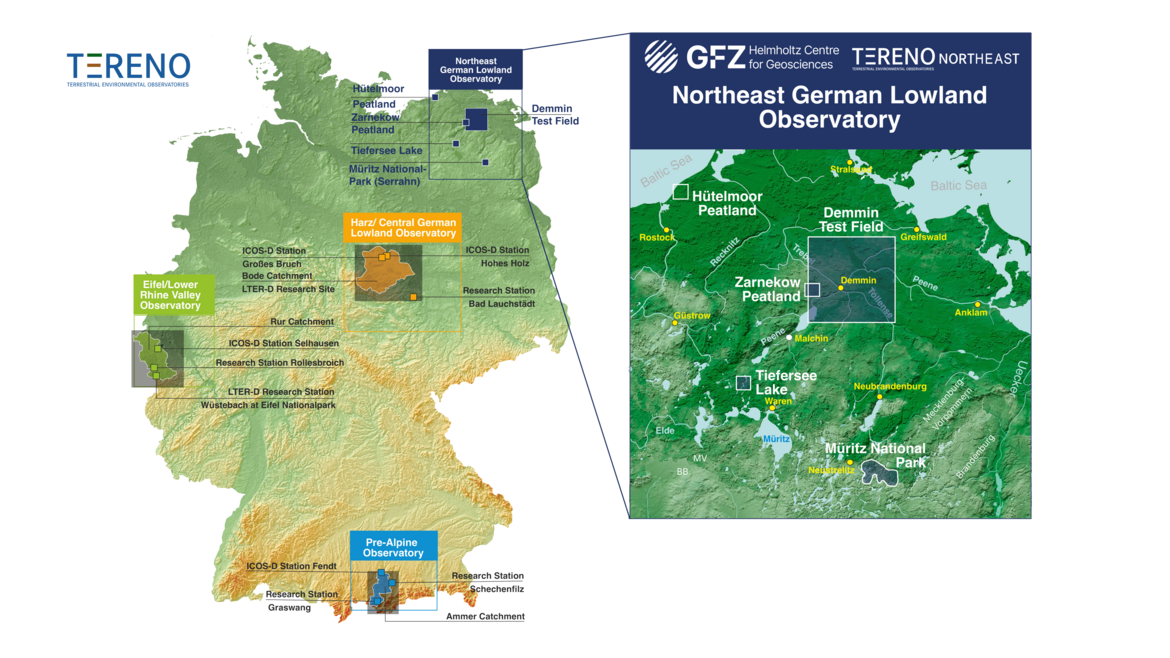
The Northeastern German Lowland observatory (TERENO-Northeast) is part of the Helmholtz Association`s interdisciplinary, long-term research network of Terrestrial Environmental Observatories - TERENO representing typical landscapes in Central Europe. TERENO-Northeast represents typical northeastern German lowland landscape, including both near-natural areas like Müritz National Park and regions that are intensively influenced and managed by human activities like farming.
Northeastern Germany, where the GFZ-run observatory TERENO-Northeast is situated, is one of the regions in Germany most vulnerable to global change. The main research foci are to understand the regional impact of global change on the Earth’s surface and near-subsurface (landscape evolution, hydrology and carbon budget) and, in turn, the influence of the Earth’s surface on atmosphere and climate via greenhouse gas fluxes. Current observations through extensive monitoring are linked with long-term proxy time series based on paleoclimate archives such as lake sediments and tree ring chronologies. This allows us to evaluate recent trends in the context of long-term temporal variability of the systems at hand. Investigations of long time series of climate change and landscape evolution are based on the hypothesis that observed recent trends can be reliably evaluated only in the context of profound knowledge of long‐term trends and their underlying processes.
Categories
Disciplinary Keywords
Instrumentation
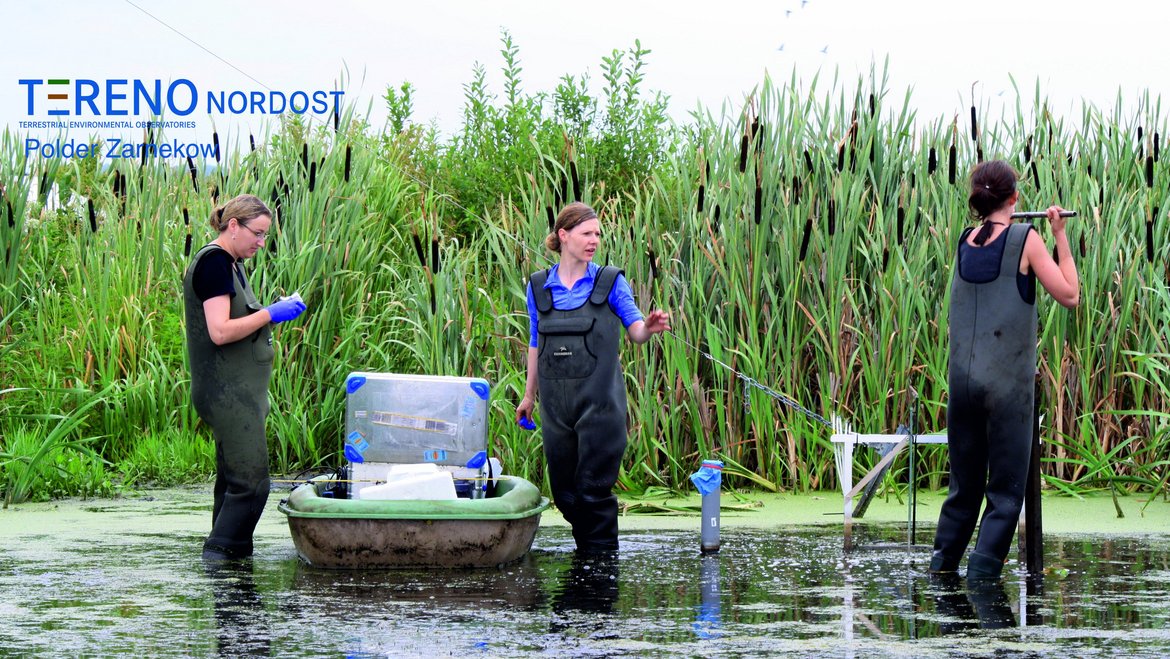
Sensors and Infrastructure
-
Eddy covariance flux towers: Equipped with sonic anemometers, fast high-precision gas analyzers with open and/or closed measurement path (H2O, CO2, CH)
-
Meteorological stations: A network of meteorological stations that provide air and ground temperature, relative humidity, air pressure, precipitation, wind direction and speed, incoming and outgoing short- and long-wave radiation
-
Water Storage Dynamics: Monitoring the dynamics of water storage by terrestrial in-situ gravimetry
-
Cosmic Ray Neutron Sensors: Using cosmic rays and and GNSS reflectometry to measure soil moisture in the ground. It utilises the interaction between cosmic rays and soil to estimate the water content in the soil over large areas.
-
Groundwater Monitoring Network
-
Precipitation and canopy shielding: Monitoring canopy shielding by measuring precipitation and stemflow with high temporal resolution in 7 different forest stands
Links
Data Access via
Scientific Publications
Relationships
- is related to