IPOC - Integrated Plate Boundary Observatory Chile
Contact:
Web:
Infrastructure belongs to:
IPOC is an international network of institutions and scientists organising and operating a distributed system of instruments and projects dedicated to the study of the subduction system, its role in landscape evolution, and associated geohazards at the continental margin of Chile. IPOC aims to reduce vulnerability to geological hazards by improving the scientific understanding of hazardous events through long-term observation and scientific collaboration. IPOC fosters research across disciplines, including geology, seismology, geodesy, volcanology, geomorphology, and georesources.
IPOC was established in 2006 as an international cooperation between the Chilean universities (Universidad Católica del Norte, Antofagasta, the Universidad de Chile with the associated Centro Sismológico Nacional, Santiago), French (IPGP, ENS), and German research institutions (GFZ, GEOMAR. IPOC is built upon decades of previous collaborations between Chilean, German, and French scientists.
Categories
Data Types
Disciplinary Keywords
Instrumentation
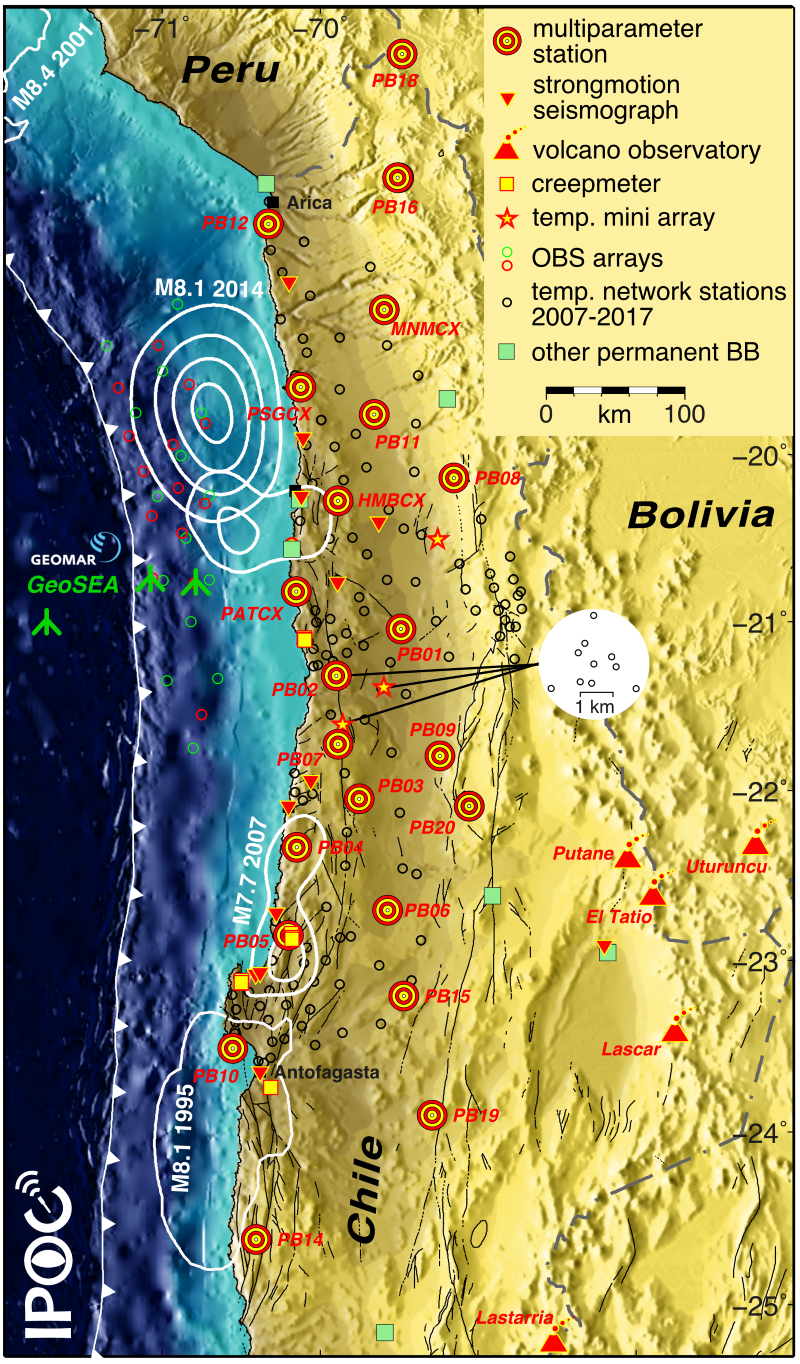
The backbone of IPOC’s monitoring capabilities is a network of currently 22 multi-sensor sites, where seismic (strong- and weak-motion), continuous GNSS (at twelve sites), magnetotellurics (at some sites), and climate data are registered at co-located sites. IPOC maintains a number of additional strong-motion and weak-motion seismographs, continuous GNSS receivers, Creepmeters, and volcano monitoring networks.
Instruments
-
Broadband Seismometers
Devices: 22 broadband seismometers at multi-parameter sites (STS-2) on QT330 (HR) digitizers; 1 Trillium Compact on EDL co-located with CAR3 creepmeter. Network code CX. Daten available under: doi:10.14470/PK615318 Access: Open
-
Cont. GNSS (Topcon T) at 12 multi-parameter sites
Devices: Cont. GNSS (Topcon T) at 12 multi-parameter sites. Plus 5 new GNSS (Septentrio Polarx) sites: 2 built, and 3 more to be built. Data available under: https://doi.org/10.5880/GFZ.1.1.2017.001 | https://doi.org/10.5880/GFZ.4.1.2017.003 Access: Variable
-
Creepmeters
Devices: 11 Creepmeters along 4 active fault segments, 3 seismometers collocated, 4 weather stations Data available under: doi.org/10.5880/GFZ.4.1.2017.002 Access: open, available on request
Data Access via
-
Magnetotelluric Stations
Devices: 11 magnetotelluric stations (fluxgate magnetometers and telluric electrodes on Earth Data Loggers). Recording at 10 multi-parameter sites and 1 additional site. To get access to data, please contact: oritter@gfz.de Access: open, available on request
-
Short-period (Mark L4-3D) on EDL offline seismic stations
Devices: 20 short-period (Mark L4-3D) on EDL offline seismic stations (Iquique local network and Pica array). Network code IQ. Data available under: doi:10.14470/VD070092 Access: Open
Data Access via
-
Strong-motion Seismometers
Devices: 24 strong-motion seismometers at 18 multi-parameter sites (Kinemetrics EPI Sensors) and 5 additional sites (Kinemetrics Etna). Network code CX. Daten available under: doi:10.14470/PK615318 Access: Open
-
Volcano fluid monitoring equipment
Devices: Volcano fluid monitoring equipment (permanent temperature sensors, time-lapse cameras, multigas sensors, and temporal experiments) Data avaible under: doi.org/10.14470/3R7569753098 │ doi.org/10.14470/7T7561754109 │ doi.org/10.5880/GFZ.2.1.2016.002 Access: on request, since 2020 the stations are maintained by Universidad Católica del Norte Antofagasta (Prof. F. Aguilera and Team)
Links
Data Access via
Project Webpage
Scientific Publications
Relationships
- is related to